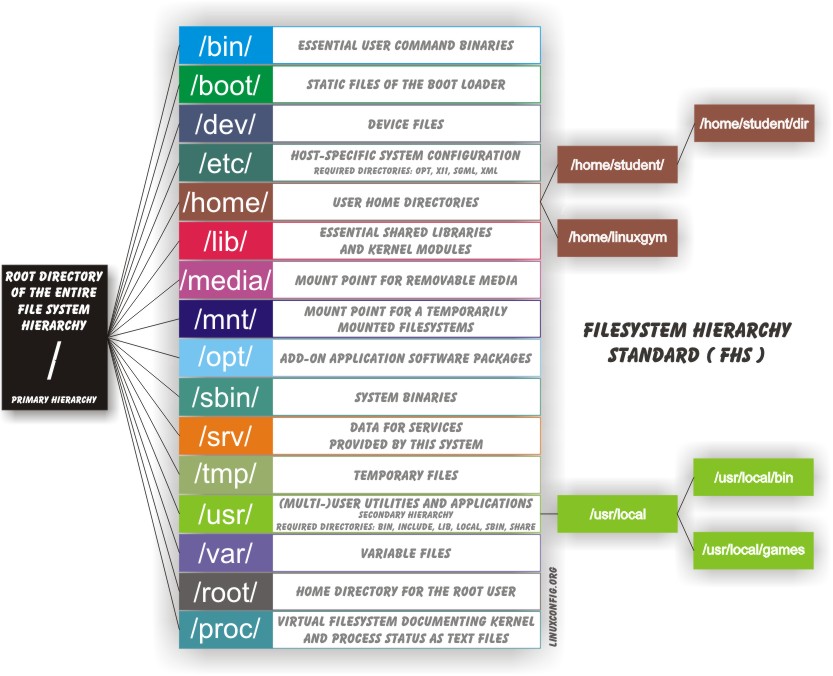
/home/
In here users home directories are located
It may be mounted on a different partition (to avoid losing data, specially in multi-user systems)
/root is the home directory of the super user
/bin and /sbin
The /bin directory contains executable binaries, essential commands used to boot the system or in single-user mode, and essential commands required by all system users, such as cat, cp, ls, mv, ps, and rm.
sbin also contains binaries but for system administration like fsck and ip
/usr/bin and /usr/sbin also exist and were different in the past. Nowadays, they are symbolically linked with /bin and /sbin
/proc
In this directory, a pseudo-filesystem is mounted (Pseudo because it has no permanent presence anywhere on the disk)
The /proc filesystem contains virtual files (files that exist only in memory) that show constantly changing kernel data.
/proc contains files and directories that mimic kernel structures and configuration information. It does not contain real files, but runtime system information. Some examples are
/proc/cpuinfo/proc/interrupts/proc/meminfo/proc/mounts/proc/partitions/proc/version
It also has sub-folders like /proc/<Process-ID-#> or /proc/sys. the information it reports is gathered only as needed and never needs storage on the disk.
/dev
Contains “device nodes”. These are files representing almost every HW and SW device (except for NW devices).
The directory is initially empty, when not mounted. udev which manages devices in linux, then creates entries dynamically when devices are found.
Some examples
sdais a hard disksda1the first partition of the disklp1second printerrandomRandom number generator
/var
The /var directory contains files that are expected to change in size and content as the system is running. Some examples are
- System log files:
/var/log - Packages and database files:
/var/lib - Print queues:
/var/spool - Temporary files:
/var/tmp
It maybe mounted in a different partition to avoid that a size overflow will damage the entire system.
/etc
This directory contains configuration files and executable scripts for system-wide configuration.
For example:
/etc/resolv.conftells the system where to go on the network to obtain host name to IP address mappings (DNS).- Files like
passwd,shadowandgroupfor managing user accounts are also found. environmentallows for configuration of environment variables
/boot
- This directory contains the file necessary to boot the OS.
- This includes files for each Kernel installed in the system (compressed kernel, files for debugging/logging)
- GRUB files are also here
/lib
Contains libraries (common code shared by executables and needed for them to run) for the essential programs in /bin and /sbin. Some distros include /lib64 for 64bit libraries (and lib has 32 bits) In newer distros, /usr/lib is symbolically linked with /lib/
/mnt, /media and /run
These directories are used for mounting external filesystems (Removable media or other) Traditionally mnt is used for mounting NW Filesystems, and others. media (and more recently run) are used to automatically mount USB drives, or any other removable filesystem when connected to the machine.
/usr
This directory contains non essential binaries, and has its own tree. Is is the user’s application space. Not for applications used by the system
/usr/includeHeader files used to compile applications/usr/libLibraries for programs in/usr/binand/usr/sbin/usr/lib6464-bit libraries for 64-bit programs in/usr/binand/usr/sbin/usr/sbinNon-essential system binaries, such as system daemons/usr/shareShared data used by applications, generally architecture-independent/usr/srcSource code, usually for the Linux kernel/usr/localData and programs specific to the local machine. Subdirectories includebin,sbin,lib,share,include, etc./usr/binThis is the primary directory of executable commands on the system